In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, staying ahead of the competition requires embracing cutting-edge technologies. One such technology that has gained significant attention is Hyperautomation. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Hyperautomation, address frequently asked questions, explore its benefits, challenges, and considerations, examine real-world case studies, discuss future trends, and emphasize its importance in the digital age.
What is Hyperautomation?
Hyperautomation refers to the integration and orchestration of various technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotic process automation (RPA), and machine learning (ML), to automate complex business processes. It extends traditional automation by combining software, robotics, and intelligent decision-making to achieve enhanced efficiency and agility. The key components of Hyperautomation include data integration, process mining, AI-driven decision-making, and workflow automation.
Benefits of Hyperautomation
- Increased efficiency and productivity: Hyperautomation eliminates manual and repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on higher-value activities. It enables faster processing, reduces cycle times, and enhances overall operational efficiency.
- Streamlined business processes and reduced errors: By automating workflows, Hyperautomation minimizes human errors and ensures consistent and accurate execution of tasks. It facilitates end-to-end process visibility, reduces bottlenecks, and optimizes resource allocation.
- Enhanced customer experience: Hyperautomation enables organizations to deliver personalized and timely services to customers. By automating customer interactions, businesses can provide self-service options, improve response times, and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Cost savings and return on investment: Through process optimization and resource allocation, Hyperautomation leads to cost reductions. By automating repetitive tasks, organizations can achieve significant time and cost savings, resulting in improved profitability and return on investment.
Challenges and considerations in implementing Hyperautomation
- Data security and privacy concerns: With the increased reliance on automation, organizations need to ensure robust data security measures and comply with privacy regulations. Protecting sensitive information and preventing unauthorized access becomes crucial.
- Workforce reskilling and change management: Hyperautomation impacts the workforce by transforming job roles and requiring new skill sets. Organizations must invest in reskilling programs to help employees adapt to the changing technological landscape.
- Integration with existing systems and legacy infrastructure: Integrating Hyperautomation with legacy systems and existing infrastructure can be complex. Organizations need to evaluate compatibility, assess integration requirements, and plan for seamless implementation.
- Scalability and adaptability to future needs: As businesses grow and evolve, scalability and adaptability become essential. Hyperautomation solutions should be designed to accommodate future expansion and support evolving business requirements.
Frequently asked questions about hyper-automation
What are the primary use cases for Hyperautomation?
Hyperautomation can be applied across various industries and functions, including finance, human resources, supply chain management, customer service, and IT operations. Use cases include invoice processing, employee onboarding, inventory management, customer support automation, and predictive maintenance.
How does Hyperautomation differ from traditional automation?
Hyperautomation extends beyond traditional automation by incorporating advanced technologies such as AI, RPA, and machine learning. It integrates systems, processes, and data across the organization to achieve end-to-end automation and intelligent decision-making.
What industries can benefit from Hyperautomation?
Hyperautomation has widespread applicability across industries, including banking and finance, healthcare, manufacturing, retail, and logistics. Any industry that relies on repetitive tasks, complex workflows, and data-intensive processes can benefit from Hyperautomation.
Is Hyperautomation suitable for small and medium-sized businesses?
Hyperautomation is not limited to large enterprises. Small and medium-sized businesses can also benefit from automation solutions tailored to their specific needs and budgets. By automating manual tasks and optimizing processes, they can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve competitiveness.
What are the potential risks or downsides of Hyperautomation?
Organizations should be cautious of potential risks, such as overreliance on automation, technological failures, and ethical considerations. Additionally, poor implementation, lack of adequate planning, and resistance to change can hinder the success of Hyperautomation initiatives.
How can businesses get started with Hyperautomation?
To begin the Hyperautomation journey, businesses should:
- Identify processes suitable for automation and prioritize based on impact and complexity.
- Assess technology options and choose a reliable Hyperautomation platform or partner.
- Develop a clear roadmap, considering implementation, employee training, and change management.
- Start with pilot projects to validate the technology and measure the benefits before scaling up.
Case studies and success stories
A real-life example of Hyperautomation is the implementation of robotic process automation (RPA) in a large financial institution.
Let’s consider a scenario where a bank processes thousands of loan applications every day. Traditionally, this process involved manual data entry, verification, and evaluation, which was time-consuming and prone to errors. However, by adopting Hyperautomation, the bank transformed its loan processing operations.
Here’s how Hyperautomation was implemented
- Intelligent Document Processing: The bank used optical character recognition (OCR) technology to extract information from various loan documents such as pay stubs, bank statements, and identification documents. The OCR software automatically scanned and digitized the documents, extracting relevant data fields like customer names, addresses, income details, and more.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): The extracted data was seamlessly integrated with RPA bots that performed tasks such as data validation, credit score checks, and background verification. These software robots were programmed to follow predefined rules and workflows, mimicking human actions within the loan processing system.
- Decision Support Systems: The bank employed machine learning algorithms to analyze the data collected from loan applications, historical data, and external sources. These algorithms helped identify patterns, predict creditworthiness, and assess risk. The decision support system provided recommendations to loan officers, aiding them in making informed decisions quickly.
- Chatbots and Natural Language Processing (NLP): To enhance customer experience and streamline the loan application process, the bank deployed chatbots integrated with NLP capabilities. Customers could interact with the chatbot via text or voice, asking questions about loan terms, eligibility criteria, or required documentation. The chatbot used NLP to understand and respond to customer queries accurately, providing real-time information and guidance.
- Integration and Workflow Orchestration: Hyperautomation facilitated the seamless integration of various systems and applications involved in the loan processing lifecycle. This allowed for data synchronization, automated notifications, and streamlined workflows across multiple departments within the bank, reducing manual handovers and improving operational efficiency.
- By leveraging Hyperautomation, the bank achieved significant improvements in its loan processing operations. The entire process became faster, more accurate, and less reliant on human intervention. Loan applications were processed with minimal errors, resulting in reduced turnaround times and improved customer satisfaction. Moreover, the bank experienced cost savings by eliminating manual labour and optimizing resource allocation.
Future trends and considerations
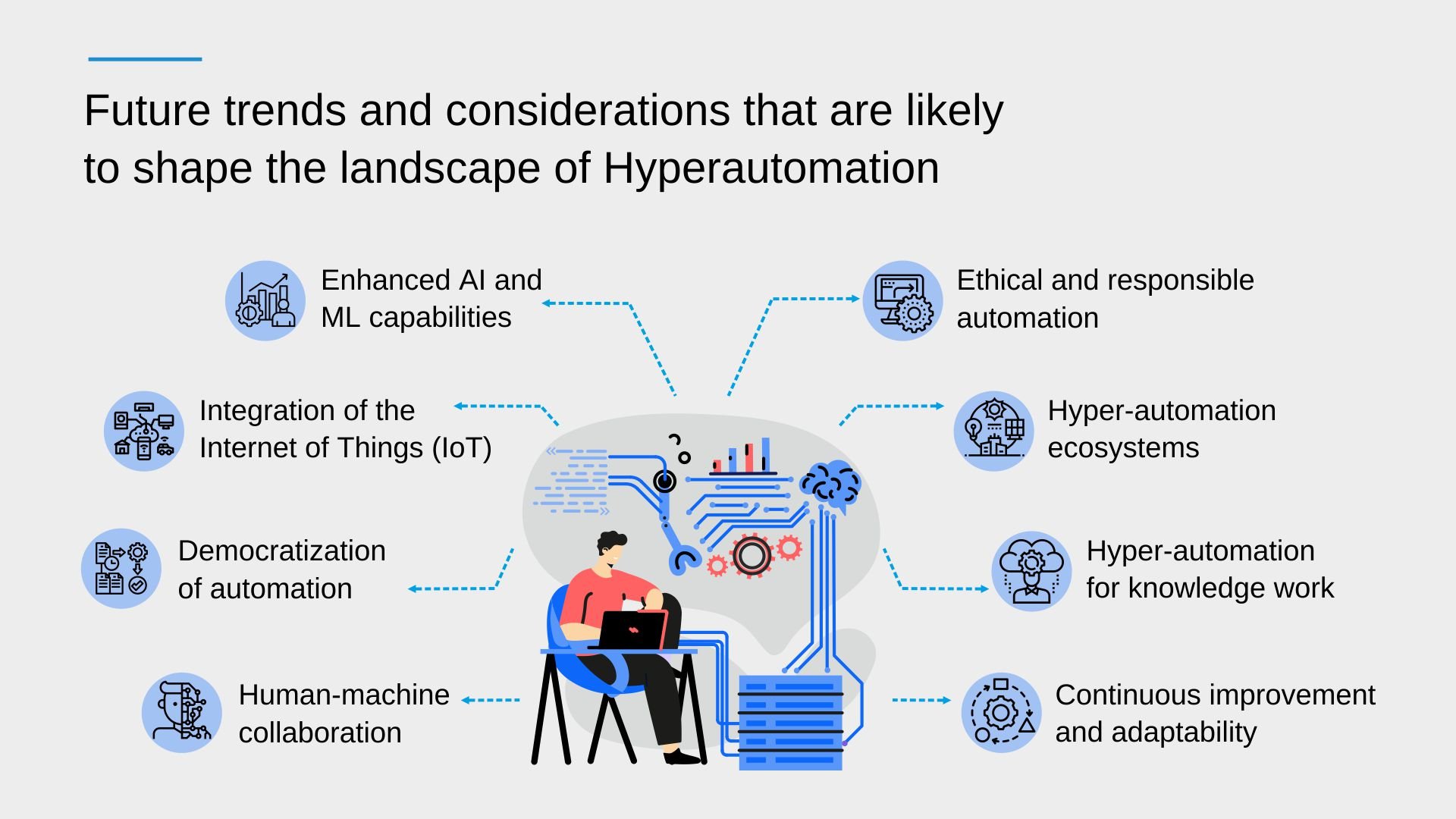
As we look into the future, several trends and considerations are likely to shape the landscape of hyper-automation. Let’s explore some of them:
- Enhanced AI and ML capabilities: AI and ML algorithms are continuously evolving, becoming more sophisticated and capable of handling complex tasks. In the future, we can expect hyper-automation solutions to leverage advanced AI and ML techniques for better decision-making, pattern recognition, and predictive analytics.
- Integration of the Internet of Things (IoT): The integration of IoT devices with hyper-automation systems will enable seamless connectivity and data exchange between physical objects and automated processes. This integration will provide real-time insights and enable automation based on the data collected from sensors, wearables, and other IoT devices.
- Democratization of automation: As hyper-automation technology matures, it is likely to become more accessible and user-friendly. Organizations of all sizes will be able to adopt and implement automation solutions without requiring extensive technical expertise. This democratization will accelerate the adoption of hyper-automation across industries.
- Human-machine collaboration: Instead of replacing humans, hyper-automation will focus on augmenting human capabilities. The future will witness the increased collaboration between humans and automated systems, where humans provide creativity, judgment, and empathy, while machines handle repetitive, mundane, and data-driven tasks. This collaboration will lead to higher productivity, efficiency, and innovation.
- Ethical and responsible automation: With the growing reliance on automation, there will be a greater emphasis on ethical considerations and the responsible use of hyper-automation. Organizations will need to address issues such as data privacy, security, bias in algorithms, and the impact on the workforce. Responsible automation frameworks and regulations will be developed to ensure fair and transparent use of hyper-automation technologies.
- Hyper-automation ecosystems: The future will witness the emergence of hyper-automation ecosystems comprising a diverse range of technologies, tools, and platforms. These ecosystems will enable seamless integration and interoperability among different automation components, allowing organizations to create comprehensive end-to-end automation solutions.
- Hyper-automation for knowledge work: While hyper-automation has predominantly been applied to repetitive, rule-based tasks, the future will see its expansion into knowledge work. Complex tasks that require cognitive skills, such as data analysis, decision-making, and problem-solving, will be automated using AI-powered systems. This will enable organizations to leverage the full potential of their workforce by focusing on high-value strategic activities.
- Continuous improvement and adaptability: Hyper-automation systems will evolve from static, predefined processes to dynamic and adaptive ones. They will continuously learn, adapt, and optimize based on real-time feedback, enabling organizations to respond quickly to changing business conditions and requirements.
Conclusion
In an era driven by digital transformation, Hyperautomation is a pivotal technology that offers organizations unprecedented efficiency, agility, and competitiveness. By understanding the fundamentals of Hyperautomation, its benefits, challenges, and future trends, businesses can harness its potential to drive growth and success. As organizations embark on their Hyperautomation journey, careful planning, strategic implementation, and ongoing evaluation will ensure optimal outcomes and pave the way for a future of improved efficiency and customer-centricity.
Topics: technologies, IoT, Hyperautomation, Mobile App Development, workflow automation, AI