In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, technological advancements are revolutionizing various industries, including retail. One such innovation is Robotic Process Automation (RPA), which involves automating repetitive and rule-based tasks using software robots. This article explores the use cases of RPA in the retail industry, highlighting its benefits, impact, and future prospects.
Automation in the Retail Industry
Importance of automation in retail
Automation plays a crucial role in the retail sector, enabling organizations to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance customer experiences. It helps retailers stay competitive in an increasingly digital world.
Advantages of RPA in the retail sector
RPA offers several advantages to the retail industry, including increased productivity, reduced costs, minimized errors, improved accuracy, and enhanced scalability. It allows retailers to focus on strategic activities while robots handle repetitive tasks.
Integration of RPA with existing systems
RPA can be seamlessly integrated with existing systems and applications in the retail industry. It works alongside legacy software and complements other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML).
Use Cases of RPA in Retail
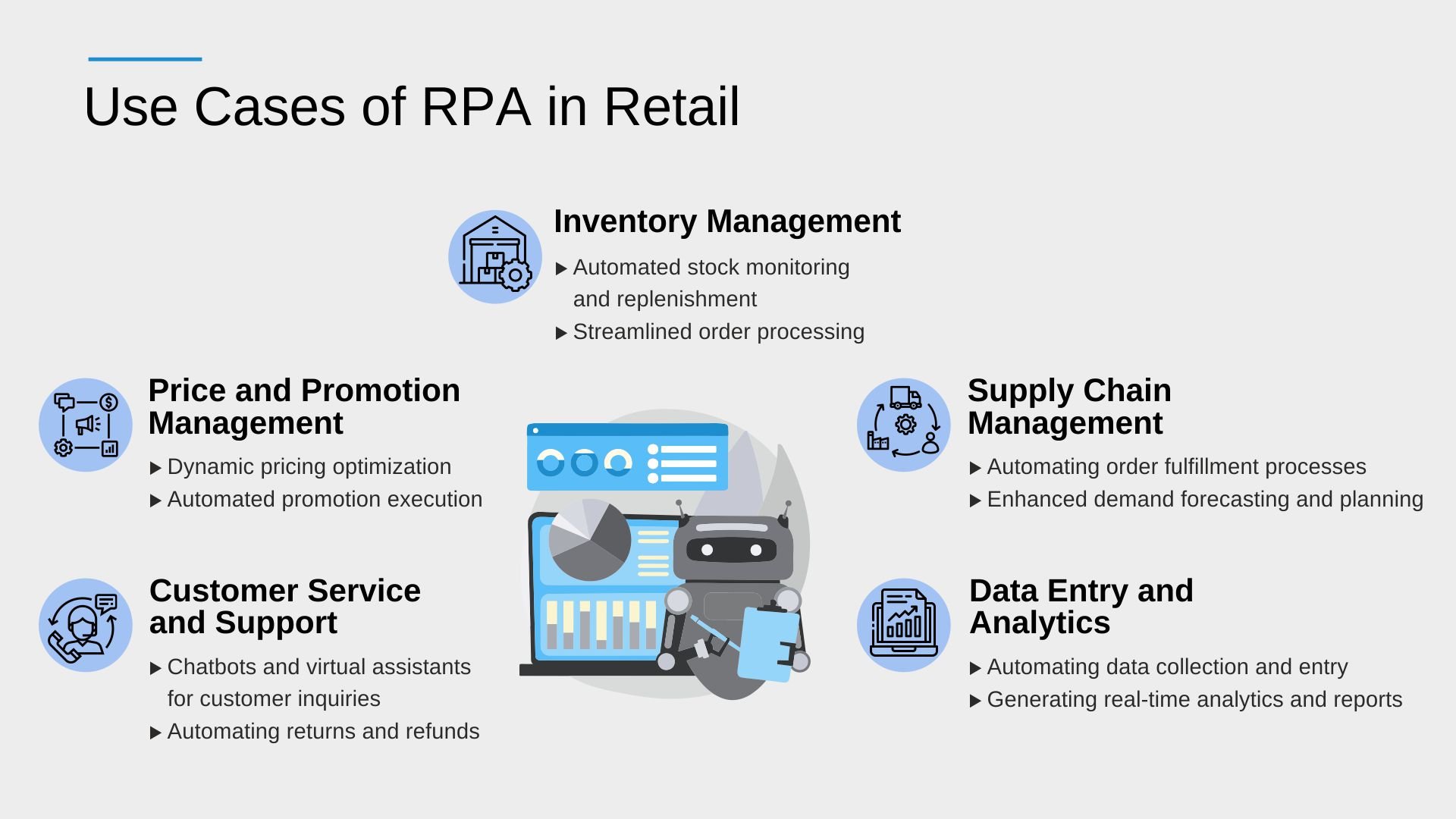
Inventory Management
- Automated stock monitoring and replenishment: RPA can monitor inventory levels in real-time, trigger automatic reordering, and update stock databases, ensuring optimal inventory levels and minimizing stockouts or excess inventory.
- Streamlined order processing: RPA can automate order processing, including order verification, invoice generation, and payment reconciliation. It reduces manual errors and accelerates order fulfillment.
Price and Promotion Management
- Dynamic pricing optimization: RPA can collect market data, analyze competitor prices, and adjust prices dynamically based on predefined rules. It enables retailers to respond quickly to market trends, optimize pricing strategies, and maximize profitability.
- Automated promotion execution: RPA can automate the execution of promotional campaigns, including applying discounts, updating prices, and generating promotional content. It ensures consistency and accuracy across multiple channels.
Customer Service and Support
- Chatbots and virtual assistants for customer inquiries: RPA-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle customer inquiries, provide personalized recommendations, and assist with product information. They enhance customer satisfaction and reduce response time.
- Automating returns and refunds: RPA can automate the returns and refund process by validating return requests, generating return labels, and updating inventory and financial systems. It simplifies the process for customers and improves operational efficiency.
Supply Chain Management
- Automating order fulfillment processes: RPA can automate various supply chain activities, such as order routing, picking and packing, and shipment tracking. It improves order accuracy, reduces fulfillment time, and enhances customer experience.
- Enhanced demand forecasting and planning: RPA can collect and analyze data from multiple sources to generate accurate demand forecasts. It helps retailers optimize inventory levels, minimize stockouts, and improve supply chain efficiency.
Data Entry and Analytics
- Automating data collection and entry: RPA can automate data extraction from invoices, receipts, and other documents, reducing manual data entry efforts. It ensures data accuracy, accelerates processes and enables real-time data analysis.
- Generating real-time analytics and reports: RPA can analyze data, create reports, and provide insights in real-time. It empowers retailers with actionable information for decision-making, trend analysis, and performance monitoring.
Benefits and Impact of RPA on Retail
Cost reduction and efficiency improvement
RPA eliminates manual and repetitive tasks, reducing labor costs and freeing up employees to focus on higher-value activities. It also improves process efficiency and reduces operational cycle times.
Enhanced accuracy and reduced errors
By automating processes, RPA minimizes human errors and ensures consistency and accuracy in retail operations. It eliminates data entry mistakes, improves inventory accuracy, and enhances customer satisfaction.
Improved customer experience and satisfaction
RPA enables retailers to provide seamless and personalized customer experiences. Chatbots and virtual assistants offer round-the-clock support, quick responses, and relevant recommendations, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Employee empowerment and resource optimization
RPA takes over mundane tasks, enabling employees to concentrate on strategic initiatives, innovation, and customer engagement. It maximizes human potential, promotes skill development, and optimizes resource allocation.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementation and integration challenges
Implementing RPA in retail may face challenges related to identifying suitable processes, designing effective automation workflows, and ensuring compatibility with existing systems. Proper planning and collaboration with IT teams are essential.
Data security and privacy concerns
RPA involves handling sensitive customer data, which requires robust security measures. Retailers must ensure data protection, and compliance with regulations like GDPR, and implement encryption and access control mechanisms.
Change management and employee adoption
Introducing RPA may require change management efforts to address employee concerns, provide training, and foster a culture of automation. Employees need to understand the benefits and embrace the technology for successful adoption.
Scalability and flexibility considerations
As the retail industry evolves, scalability and flexibility become crucial. Retailers should choose RPA solutions to accommodate future growth, integrate with emerging technologies, and adapt to changing business requirements.
Future Trends and Opportunities
Advancements in RPA technology
RPA technology continues to evolve, with advancements in areas like natural language processing (NLP), optical character recognition (OCR), and cognitive automation. These advancements will enable more sophisticated automation capabilities in the retail industry.
RPA in e-commerce and omnichannel retailing
E-commerce and omnichannel retailing are gaining prominence. RPA can streamline order processing, inventory synchronization, and customer service across multiple channels, enabling retailers to deliver a seamless shopping experience.
RPA and artificial intelligence (AI) integration
The integration of RPA with AI technologies like ML and NLP opens up new possibilities. AI-powered chatbots and cognitive automation can understand customer intents, process unstructured data, and deliver more intelligent responses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, RPA is transforming the retail industry by automating repetitive tasks, improving operational efficiency, and enhancing customer experiences. From inventory management to customer service and analytics, RPA offers numerous use cases that deliver benefits such as cost reduction, improved accuracy, and empowered employees. However, challenges related to implementation, security, change management, and scalability need to be carefully addressed. By embracing RPA and staying abreast of future trends, retailers can gain a competitive edge and thrive in the digital era.
Topics: technologies, IoT, Hyperautomation, Mobile App Development, workflow automation, AI